3 // Local Deployment
This page covers setting up Python, Dagster, dbt, and Soda for local development. Dagster is introduced early so that the pipelines can be run first. dbt and Soda require data in Supabase to function, so this order lets each tool be tested as the page progresses.
The 4. AWS section will show how to deploy this solution on the cloud.
Python
First, create a directory for all the Python code. This project's Python directory is called card_data.
Once the directory is created, cd into it from the terminal.
All following commands will take place in this directory.
Installing uv
uv is the main package and project manager used in this project. Learn more about uv.
- Install via their installation script: or brew:
-
Install Python with
uv: -
Initialize
uvto set up project files. This will create apyproject.tomlfile if one does not already exist: -
Sync
uvwith the libraries fromcard_data/pyproject.toml. Syncing ensures that all project dependencies are installed and up-to-date with the lockfile.
ELT Files
The files used for extracting, loading, then transforming the data all live in the pipelines/defs/ directory.
At the time of writing, the extract/ and load/ directories have 2 different files aimed at calling different APIs.
One for card data from tcgdex and the other for pricing data from tcgcsv.
.
└── pipelines/
└── defs/
├── extract/
│ ├── extract_data.py
│ └── extract_pricing_data.py
├── load/
│ ├── load_data.py
│ └── load_pricing_data.py
└── transform/
└── transform_data.py
Dagster
What is Dagster?
Dagster is an open-source data orchestration tool that helps you build, run, and monitor your data pipelines. It’s designed to make working with data workflows more reliable and maintainable, giving you clear visibility into each step and making it easier to catch issues before they cause problems.
View more about Dagster
Configuring
Dagster and its components needed for the project can be installed with uv:
This will add the libraries to pyproject.toml file.
To run the Dagster service and web server, run the following in the correct directory with .venv active:
The web UI can be viewed at http://127.0.0.1:3000
Running the Pipelines
With Dagster running, the pipelines can be triggered to populate data in Supabase. This step is required before dbt or Soda will work since both tools expect data to already exist in the staging tables.
This project currently has 4 pipelines: * Card data * Set data * Series data * Pricing data
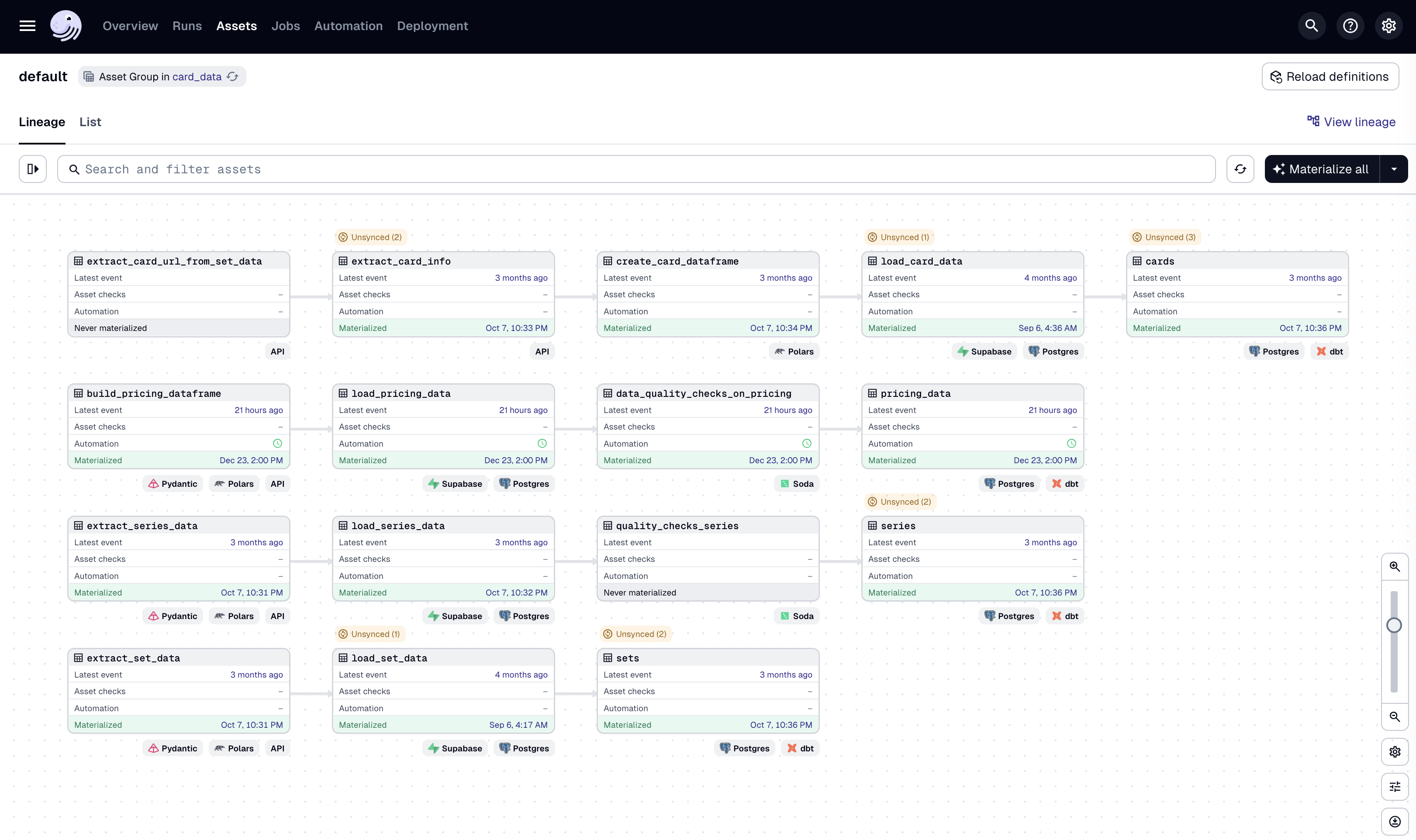
- Open the Dagster UI at
http://127.0.0.1:3000. - On the top bar, click on Assets.
- Select the assets to materialize. For initial setup, select:
extract_series_dataextract_sets_dataload_series_dataload_set_data
- Click Materialize selected in the top right.
- Monitor the run in the Runs tab. Once complete, the data will be available in the Supabase
stagingschema.
Note
The load assets depend on extract assets, so Dagster will automatically run them in the correct order.
dbt (Data Build Tool)
What is dbt?
dbt (data build tool) is a command-line tool that enables data analysts and engineers to transform data in warehouses using SQL. The tool allows users to write modular SQL queries as "models" that build upon each other, automatically managing dependencies and enabling version control, testing, and documentation of data transformations. dbt compiles SQL models into executable queries and runs them in the proper order, turning raw data into analysis-ready datasets.
View more about dbt
Installation & Initialization
Install with uv:
This will add the libraries to pyproject.toml file.
Initialize a dbt project in the card_data directory:
Follow the prompts to finish setting up the dbt project.
Models
Models are the pieces of SQL code that run when using that dbt build command that build the
tables to the destination schema. In this project, that would the public schema in the PostgreSQL
database on Supabase.
The public schema is the public facing schema that exposes the API to the data in the tables.
Sources
Create a sources.yml file under the models/ directory.
More info on sources here.
This file is used to declare and configure the raw data sources. These tables are the foundation for the dbt models but are not managed by dbt itself.
For example:
sources:
- name: staging
description: "Staging schema containing raw data loaded from extract pipeline"
tables:
- name: series
description: "Pokemon card series data"
columns:
- name: id
description: "Unique series identifier"
- name: name
description: "Series name"
- name: logo
description: "Series logo URL"
The above yml defines the structure for the raw series table from the staging schema.
Soda
What is Soda?
Soda is a data quality platform that helps monitor, test, and validate data in warehouses, lakes, and pipelines. It uses a simple YAML-based language (SodaCL) to define data quality checks— like testing for null values, schema changes, freshness issues, or anomalies—and runs them automatically on your data sources. Soda integrates with popular data platforms (Snowflake, BigQuery, Postgres, etc.) and can alert when data quality issues are detected, helping catch problems before they impact downstream analytics or ML models.
View more about Soda
Configuring & Running
Soda and its components needed for the project can be installed with uv:
-
Install Soda Core with PostgreSQL connector since Supabase uses PostgreSQL. Other connectors can be used.
-
Create a
configuration.ymlandchecks.ymlfiles under thecard_data/pipelines/soda/directory.-
The
configuration.ymlholds the information for connecting to the data source. The below is an example from this project that reads theusernameandpasswordfrom the local environment so that this file can be safely committed togitand pushed to GitHub. -
The
checks.ymlfile is where the data quality checks are defined. The below is an example from this project of simple checks being performed on theseriestable in the staging database.checks for series: # Row count validation - row_count = 4 # Schema validation checks - schema: fail: when required column missing: [id, name, logo] when wrong column type: id: text name: text logo: text # Completeness checks (no null values) - missing_count(id) = 0 - missing_count(name) = 0 - missing_count(logo) = 0 # Data uniqueness checks - duplicate_count(id) = 0 - duplicate_count(name) = 0 # Data format validation - URL pattern check - invalid_count(logo) = 0: valid regex: '^https://.*'
-
-
Once the files are created, set the environment variables for
${SUPABASE_USER}and${SUPABASE_PASSWORD}. These can be found from the connection string as shown in 2 // Supabase: -
Run a scan by referencing the correct path to both files:
-
Review the output. Running these checks on this project results in:
[15:25:38] Soda Core 3.5.5 [15:25:40] Scan summary: [15:25:40] 8/8 checks PASSED: [15:25:40] series in supabase [15:25:40] row_count = 4 [PASSED] [15:25:40] Schema Check [PASSED] [15:25:40] missing_count(id) = 0 [PASSED] [15:25:40] duplicate_count(id) = 0 [PASSED] [15:25:40] missing_count(name) = 0 [PASSED] [15:25:40] duplicate_count(name) = 0 [PASSED] [15:25:40] missing_count(logo) = 0 [PASSED] [15:25:40] invalid_count(logo) = 0 [PASSED] [15:25:40] All is good. No failures. No warnings. No errors.